Luxation / Subluxation (Dislocated Elbow)
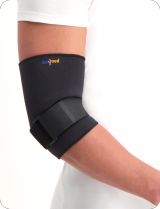
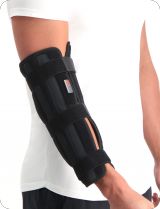
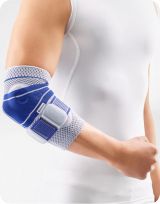
Dislocated your elbow? Then take a look at our elbow support products. Tested and selected by our Medical Team. Prefer additional information? Feel free to read on, we're more than happy to explain it to you.
Read more »General information
A dislocated elbow is an injury that's recognizable by damage and a rupture of the connective tissue around the elbow joint. Furthermore, the bones in the joint are dislocated, which litteraly means that your bones are no longer in their natural position. A dislocated elbow can form a serious elbow injury. While making certain movements with your elbow, your elbow gets put onder heavy pressure. If this happens too often, the connective tissue (capsular ligaments and other ligaments) can tear. If this pressure is more than the muscles and bones can bear, this can cause dislocation. In that case, the bones will move shift from their natural position and that process is called a dislocated elbow. Because this takes a lot of force, a dislocation is usually accompanied by other injuries.
Causes
A dislocated elbow is usually caused by a trauma that forces the bones of your elbow to get pushed apart. This can occur during contactsports or by falling while your arm is stretched.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a dislocated elbow are:
- Sudden severe pain at the moment of the trauma
- The person can't go on with the activity and clamps around the elbow to protect it
- The pain is felt in the elbow region but can also be felt in the lower arm, hand or fingers
- The person often has the feeling as if the elbow dislocates
- Swelling and visible changes in the shape of the elbow joint can be seen when you compare your arms
- In time, a bruising can occur
- The pain increases when the elbow is touched
- When and if the swelling increases, you will no longer be allowed to fully bend and stretch your arm
Sometimes, a tingling and numb feeling can be felt
In some cases, the pulse can no longer be felt
Treatment
Usually, the patient's story combined with a clinical examination by a specialist is enough to confirm the diagnosis. Further investigation like a CT or MRI scan can also help in the determination of the seriousness of the injury. An RX scan can also be taken after the elbow has been replaced back in his natural position by a specialist. A dislocated elbow needs immediate medical assistance. In some cases, the blood vessels can be damaged by the dislocation. If the pulse is absent, immediate relocation is required to restore the blood flow. If it is still absent after the relocation, you will immediately need a surgical intervention.
Persons without compression of the blood vessels are examined with an RX scan. This eliminates possible fractures before the elbow joint is relocated to its natural position. The relocation of the elbow may never be done by the person himself, if this is not done properly, nerves, blood vessels, bones, ligaments and cartilage could get seriously damaged. Visiting an orthopedic surgeon is necessary for an optimal recovery. This treatment can consist of: immobilization, wearing a brace, surgery or relocation of dislocated bones. The orthopedist will decide what the appropriate treatment will be, based on the injury. After relocating the elbow, the patient will undergo an intensive physiotherapy rehabilitation program. This is necessary to get the best possible outcome for the recovery process, avoiding recurrance of the injury. This treatment can consist of:
- Triggerpoint therapy
- Dry-needling therapy
- Medical taping
- Soft tissue massage
- Elektrotherapy or Hydrotherapy
- Hot & Cold therapy
- Training and adjusted exercises
- Joint mobilization
- Wearing a brace / splint: Super Ortho Elbow / Lower Arm Splint